Refining Your Idea Before Talking with a Sample Maker
Conducting thorough market research is fundamental for aligning your product ideas with market needs and consumer expectations. To ensure accuracy and clarity in your research, follow this refined approach:
Steps to Conduct Comprehensive Market Research
Define Research Objectives
First, clearly articulate what you want to discover through your market research. Whether identifying consumer preferences, analyzing competitive products, or understanding emerging market trends, having precise objectives will guide your research methodology and data collection efforts.
Select Research Methods
To gather the necessary data, you’ll need to employ various research methods:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Utilize platforms like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms to collect quantitative data about consumer preferences, behaviors, and demographics.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews to gain deeper insights into consumer motivations and detailed feedback on your product concepts.
- Focus Groups: Organize sessions with targeted consumer groups to discuss and gauge reactions to your product ideas, offering rich qualitative data.
- Observational Research: Observe how potential customers interact with existing products in real-world and controlled environments to gather contextual insights.
Data Collection
Next, employ the selected methods to compile data, ensuring your sample accurately represents your target demographic. Incorporate digital analytics tools like Google Analytics to analyze user behavior on your digital platforms. Use the analytics tools provided by the platforms themselves for insights into social media engagement.
Data Analysis
After gathering your market research data, the next critical step is to analyze it to uncover actionable insights. This analysis is split into two main types: quantitative and qualitative data analysis.
1. Quantitative Data Analysis:
Begin with your quantitative data, which includes all numerical data collected from surveys, questionnaires, and digital analytics. Utilize statistical tools like SPSS or Excel to sift through this data. These tools are instrumental in identifying patterns, trends, and correlations that can provide a statistical basis for your decisions. For example, you might discover a significant preference for a particular product feature across various demographics, which could guide the development priorities.
2. Qualitative Data Analysis:
Once you’ve identified quantitative trends, shift your focus to qualitative data. This data comes from more narrative sources, such as interviews and focus groups. Perform thematic analysis to extract deeper insights and sentiments your target audience expresses. This process involves coding the data to identify common themes and ideas that recur across your interviews or discussion sessions. These insights can be particularly valuable in understanding the reasons behind consumer behaviors and preferences, adding depth to the numerical data collected.
By integrating quantitative and qualitative analyses, you ensure a comprehensive understanding of the statistical trends and human elements behind your data. This dual approach allows you to effectively refine your product design and marketing strategies, ensuring they are well-tuned to meet your market’s needs and desires.
Apply Insights to Product Development
Finally, integrate the insights obtained into refining your product design, feature set, and marketing strategies. Ensure your product is tailored to meet consumer needs and stand out against competitors.
Tools and Resources for Effective Market Research
- SurveyMonkey or Google Forms: These tools are efficient for crafting and distributing surveys quickly and analyzing responses.
- Google Analytics: Ideal for tracking user behavior and engagement on your websites and e-commerce platforms.
- SEMrush or Ahrefs: These tools are typically used for SEO and digital marketing but can provide valuable insights into market trends and competitive analysis. They can help you understand how competitors are positioning their products and the keywords they are targeting.
Consider engaging with professional market research firms for more specialized market research, especially if in-house capabilities are limited or the market landscape is particularly complex. Companies like Nielsen or Mintel offer comprehensive market analysis services tailored to specific industries and can provide deep, actionable, relevant insights.
Following these steps and utilizing the right tools will make your market research more robust. This will provide a solid foundation for product development closely aligned with market dynamics and consumer preferences. This approach ensures that your product development process is informed by accurate and actionable data, maximizing your product’s potential for success in the market.
Defining Your Product Concept
Once you understand the market, the next step is to define your product concept. This involves translating the insights gathered from your market research into a detailed and actionable product concept.
Key Elements to Define Your Product Concept:
- Product Features: Decide on the unique features that will differentiate your product.
- Functionality: Ensure the product performs its intended function effectively.
- Aesthetics: Consider the visual aspects of the product, which are crucial in the soft goods market.
When refining your product concept for the soft goods industry, clarifying and distilling your initial ideas into a comprehensive, coherent concept that resonates with your target audience and the sample maker is crucial. Here’s how you can expand your process for defining your product concept, including a template to help structure your thoughts.
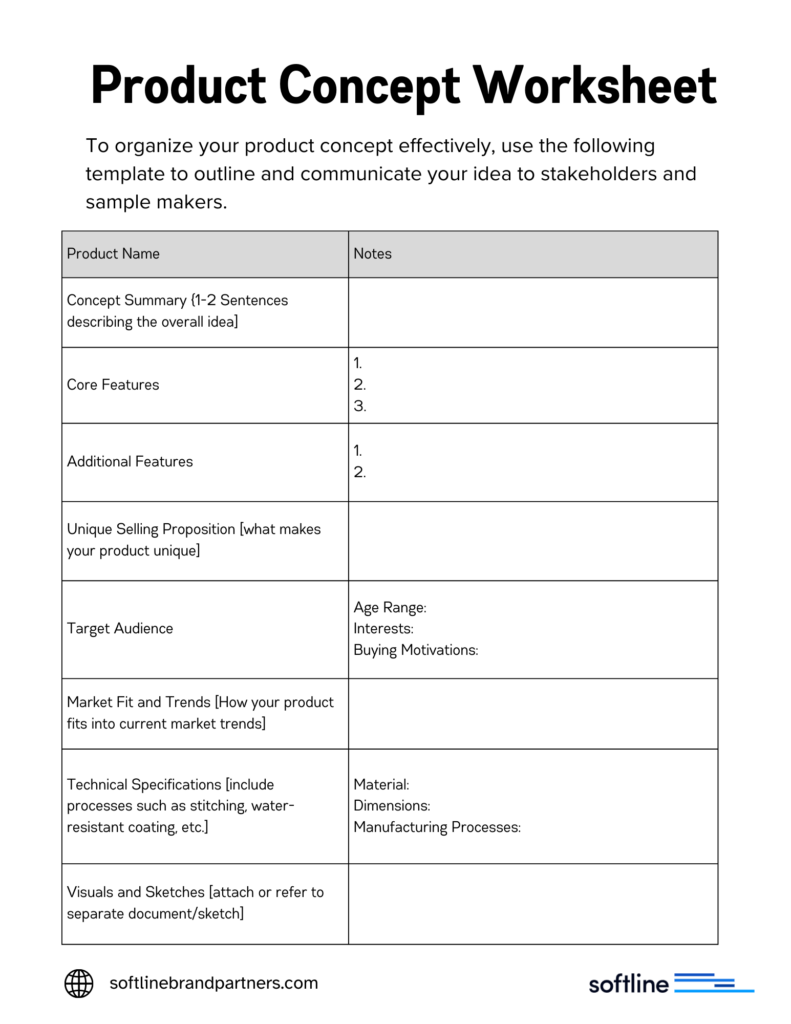
Download the Product Concept Worksheet
Steps to Define Your Product Concept:
- Concept Summary: Start with a clear and concise statement that captures the essence of your product. This should include the product, who it is for, and what unique needs it addresses.
- Feature Breakdown:
- Core Features: List the key features of your product. These are the non-negotiable elements that define your product.
- Additional Features: Identify secondary features that enhance your product’s appeal or functionality but are not essential.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what makes your product different from and better than the competition. This could relate to design, materials, cost, efficiency, or innovation.
- Target Audience: Define who your product is intended for. Include demographic and psychographic details that help tailor the design to meet their needs and preferences.
- Market Fit and Trends: Analyze how your product fits current market trends. Adjust your concept to leverage these trends while ensuring that it remains timeless.
- Technical Specifications: Detail the materials, dimensions, and manufacturing processes involved. This will be critical for the sample maker to understand and create your product accurately.
- Visuals and Sketches: Provide preliminary sketches or digital renderings of your product. Visuals are crucial for conveying your design intentions clearly.
Creating a Design Brief
The design brief should ideally be prepared and presented to the sample maker before your initial meeting. This document is a fundamental communication tool that outlines your project’s requirements, goals, and specifics about the product you want to create. Presenting a complete and detailed design brief during your first interaction with the sample maker ensures that your product’s key elements are clearly understood from the outset. This clarity helps the sample maker grasp your vision and requirements, facilitating a more accurate and efficient sample development.
By providing the design brief at the beginning of your collaboration, you can set clear expectations, reduce misunderstandings, and streamline the production process. This approach helps achieve a prototype that closely matches your specifications but also aids in maintaining project timelines and budgets.
If changes are necessary after feedback from the sample maker or further development insights, the design brief can be updated to reflect new information or adjustments. Thus, while the initial brief should be as comprehensive as possible, it should also be flexible enough to incorporate practical inputs from the sample maker, which can enhance the product’s design and functionality.
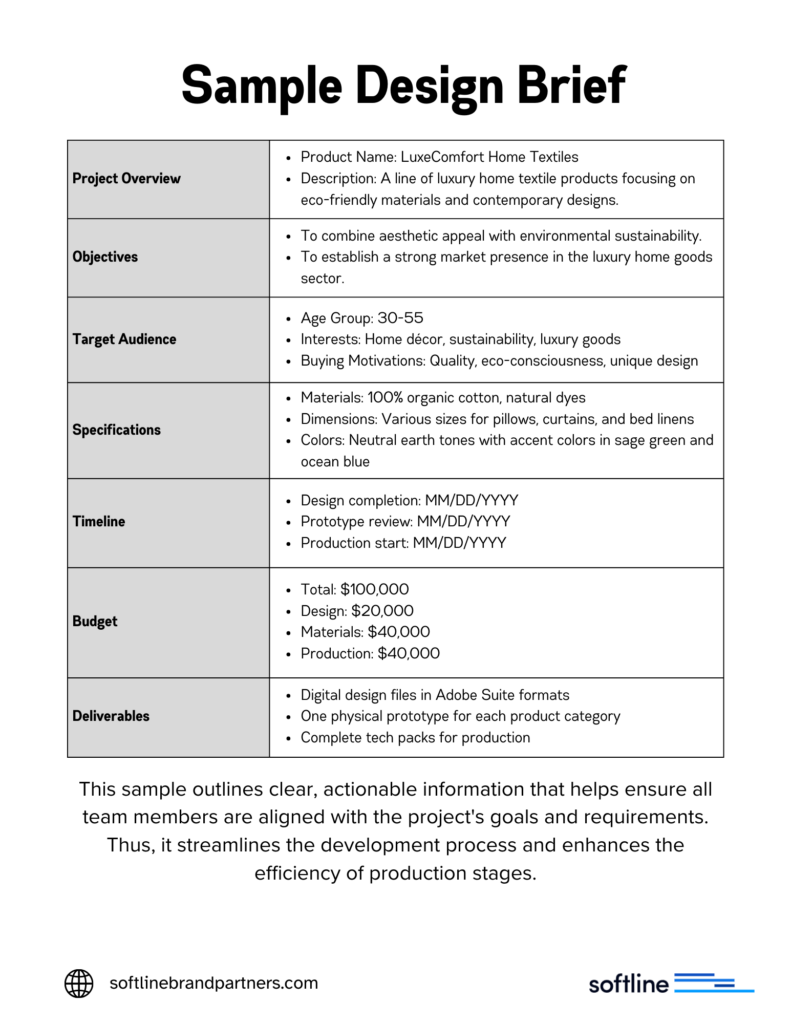
Essential Components of a Design Brief
A well-crafted design brief should include:
- Project Overview:
- Begin with a clear and concise product description, including its purpose and the specific problem it solves.
- Outline the scope of the project to provide context for the teams involved.
- Objectives:
- Clearly state the goals of the project. This could include specific performance targets, aesthetic aspirations, or market positioning objectives.
- Target Audience:
- Provide detailed demographic and psychographic information about the intended end-users. This ensures that the design is tailored to meet their needs and preferences.
- Specifications:
- Provide exhaustive information about materials, dimensions, color schemes, and technical requirements.
- This section should leave no room for ambiguity and ensure all production details are meticulously documented.
- Timeline:
- Include a detailed schedule with milestones for design completion, prototype development, and final production.
- Budget:
- Outline the financial parameters within which the project must be completed. Include allocations for design, materials, and manufacturing.
- Deliverables:
- Specify the final products and files to be delivered, such as digital files, physical prototypes, and comprehensive tech packs.
By following the guidelines detailed in this sample, businesses can communicate their vision and expectations effectively, paving the way for successful product development and launch.
Developing a Tech Pack
The Tech Pack is the final document that needs to be prepared before meeting with a sample maker. Creating a tech pack is a critical step in transitioning from a product concept to a physical sample. A tech pack is a blueprint for manufacturing your product, detailing every aspect of its design and specifications. Here are some key recommendations to ensure that your tech pack is comprehensive and effectively communicates your vision to manufacturers:
- Start with a Detailed Cover Page:
- Include basic yet essential information such as the product name, style number, season, designer or brand name, and contact information.
- Clearly state the version of the tech pack if updates have been made over time.
- Include Precise Technical Sketches:
- Provide clear and detailed product sketches from multiple views (front, back, and sides).
- Create these sketches using Adobe Illustrator or similar software. They need to be precise and easily editable.
- Annotate with notes on stitching, trims, and hardware details.
- Bill of Materials (BOM):
- List all materials required for your product, including fabrics, trims, labels, threads, and hardware.
- Specify material quality, color codes, supplier information, and required quantity.
- Recommendations: Use standardized color references like Pantone codes to avoid discrepancies in color interpretation.
- Comprehensive Construction Details:
- Include detailed instructions on how each part of the product should be assembled.
- Specify stitching details, seam types, and finishing techniques.
- Recommendations: Provide photographs or diagrams for complex construction details to ensure clarity.
- Size and Measurement Specifications:
- Provide a complete size chart with measurements for each size the product will be offered in.
- Include detailed point of measure (POM) guidelines that show exactly where and how measurements should be taken.
- Recommendations: To aid in pattern making, consider including a base size sample measurement and grading rules for other sizes.
- Prototyping Feedback:
- Document any changes made during the prototyping phase, including notes on fit, materials, and construction adjustments.
- Recommendations: Always update the tech pack after each prototype to reflect any modifications, ensuring the latest version is accurate and comprehensive.
- Additional Details:
- Include information on labels, tags, packaging, and folding instructions.
- Recommendations: Detail any legal requirements for care labels or country of origin labels to ensure compliance with international standards.
- Final Review and Approval:
- Ensure that all relevant stakeholders have reviewed and approved every aspect of the tech pack before sending it to the manufacturer.
- Recommendations: Conduct a final walkthrough of the tech pack with your design and production team to ensure all information is correct and complete.
By following these guidelines and including detailed, clear information in your tech pack, you can significantly reduce the risk of errors in production and ensure that the final product meets your specifications and quality standards. A well-prepared tech pack facilitates smoother communication with manufacturers but also helps maintain consistency across production runs.
Presenting Your Concept to a Sample Maker with Softline Brand Partners
Once you have prepared your documents, you can present your product concept to a sample maker. This crucial meeting provides you with the opportunity to convey your product’s vision, functionality, and aesthetic details clearly. With the guidance of Softline Brand Partners, startups can navigate this stage more effectively, ensuring that their product’s planning and design are thoroughly aligned with industry standards.
Preparation with Softline Brand Partners
To ensure a successful meeting, collaborate with Softline Brand Partners to meticulously prepare all your documentation. This includes organizing detailed worksheets, tech packs, design sketches, and material specifications into a clear and professional presentation. Softline’s expertise in developing comprehensive tech packs ensures that all technical specifications—such as materials, dimensions, and manufacturing processes—are well-documented and easily understood. This not only respects the sample maker’s time but also sets a professional tone for the meeting.
Engaging in a Detailed Discussion
Once your documents are perfectly in order, discuss your concept with the sample maker. With support from Softline, highlight the core and additional features of your product, explaining how each attribute adds value or solves a specific problem. Emphasize your Unique Selling Proposition (USP), articulating what makes your product stand out from the competition, and focus on any innovations or unique benefits.
Softline Brand Partners will help ensure that you are prepared to receive and integrate feedback from the sample maker. Their input can provide valuable insights and highlight potential challenges that might not have been previously considered. Being open to adjustments based on this feedback is crucial for refining your product to ensure its manufacturability and market relevance.
Clarifying and refining your product idea with the help of Softline Brand Partners before meeting with a sample maker is crucial for ensuring its success. By leveraging Softline’s expertise to conduct thorough market research, define a clear product concept, and prepare a comprehensive tech pack, you can streamline the sampling process and enhance the overall quality of your final product. This preparation leads to a smoother transition from concept to market-ready product, setting the stage for your success in the competitive landscape of the soft goods industry.
Softline for Start-Ups Resource Guide
Building a Brand in the Soft Goods Market
Intellectual Property Protection in Fashion and Soft Goods
Concept to Prototype: Softline’s Design and Sampling Services










